This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Docker
Learn how to build docker images with best practices
1 - Installing Docker
How to install and setup docker
How to install Docker
# requires elevated access either root or sudo
# install required dependencies (tested on Raspberry Pi 4)
sudo apt-get -y install libffi-dev libssl-dev python3-dev python3 python3-pip
sudo curl -sSL https://get.docker.com | sh
# To run docker as non sudo/root user, add the user to docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker <user> #logout and login after this command.
# Testing
docker run hello-world
How to install Docker CE on Centos7
# Installing dockerCE
yum install -y yum-utils \
device-mapper-persistent-data \
lvm2
yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
yum install docker-ce
# post docker install steps
# to run docker as non root user
usermod -aG docker <user_id>
[root@centos7vm ~]# systemctl enable docker
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service.
[root@centos7vm ~]# chkconfig docker on
Note: Forwarding request to 'systemctl enable docker.service'.
service docker start
docker ps
Docker config file
login credentials are saved in /home/username/.docker/config.json
/var/run/docker.sock
This is an Unix socket the Docker daemon listens on by default, and it can be used to communicate with the daemon from within a container.
#Example, portainer an opensource web interface to manage containers using bind mount
$ docker container run -d \
-p 9000:9000 \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ #bind mount
portainer/portainer
Bind mounting the Docker daemon socket gives a lot of power to a container as it can control the daemon. It must be used with caution, and only with containers we can trust.
How to enable Docker Remote API on Ubuntu
sudo vi /lib/systemd/system/docker.service
# Modify the line that starts with ExecStart
ExecStart=/usr/bin/docker daemon -H fd:// -H tcp://0.0.0.0:4243
systemctl daemon-reload
sudo service docker restart
#Testing
sriram@optimus-prime:~$ curl http://localhost:4243/version
{"Platform":{"Name":""},"Components":[{"Name":"Engine","Version":"18.03.1-ce","Details":{"ApiVersion":"1.37","Arch":"amd64","BuildTime":"2018-04-26T07:15:45.000000000+00:00","Experimental":"false","GitCommit":"9ee9f40","GoVersion":"go1.9.5","KernelVersion":"4.15.0-38-generic","MinAPIVersion":"1.12","Os":"linux"}}],"Version":"18.03.1-ce","ApiVersion":"1.37","MinAPIVersion":"1.12","GitCommit":"9ee9f40","GoVersion":"go1.9.5","Os":"linux","Arch":"amd64","KernelVersion":"4.15.0-38-generic","BuildTime":"2018-04-26T07:15:45.000000000+00:00"}
2 - Best Practices
- Use official Docker images as base images
- Use specific image version
- Use small sized official images
- Optimize caching image layers
- Use
.dockerignoreto exclude unwanted files and folders - Make use of Multi-Stage builds
- Use the least priileged user to run the container
- Scan your images for vulnarabilities
3 - Building Images
Dockerfile
- Dockerfile is a simple text file to create a docker image.
- Default file name is “Dockerfile”
Example dockerfile
ENV
FROM
LABEL maintainer=""
version=""
WORKDIR
RUN
VOLUME
EXPOSE
ENTRYPOINT --> Executes custom scripts while starting a docker container
--> Do not add layer to docker image
CMD
There can only be one CMD instruction in a Dockerfile. If you list more than one CMD, then only the last CMD will take effect.
# Example dockerfile
COPY docker-entrypoint.sh /
RUN chmod +x /docker-entrypoint.sh
ENTRYPOINT ["/docker-entrypoint.sh"]
How to build a docker image
#docker image build -t <image_name>:<version_tag> .
docker image build -t ansible:v1.0 .
How to run the container
docker container run -d -t --name ansible ansible:v1.0 bin/bash
How to connect to a running container
$ docker container exec -it <container_id> bash
# (or) to run shell command directly on a running container, then
$ docker container exec <container_name/id> cat /appl/readme.txt
Data persistance and volume sharing between running containers
In docker, sharing of volumes can be done in 2 ways
- Add VOLUME in dockerfile , example VOLUME [/appl]
- [or] Add -v <volume_path> as a flag while running the container to expose the path, example below
If volume is exposed in either of the above methods, then both the src and dst containers should run on the same physical host
docker container run --rm -itd --name <container_name> -v $PWD:/appl -v /appl/data
Inorder to access data from other containers, use volumes-from flag while running the container
docker container run --rm -itd --name <dest-container> --volumes-from <src_container_name_from_which_data_is_accessed>
optimizing docker images
.dockerignore
Useful docker commands
# To stop all running containers in one go, below command can be used
docker container stop $(docker container ls -a -q)
References
Detailed Explanation of Dockerfile
Best practices for writing Dockerfiles
Video References
4 - Networking
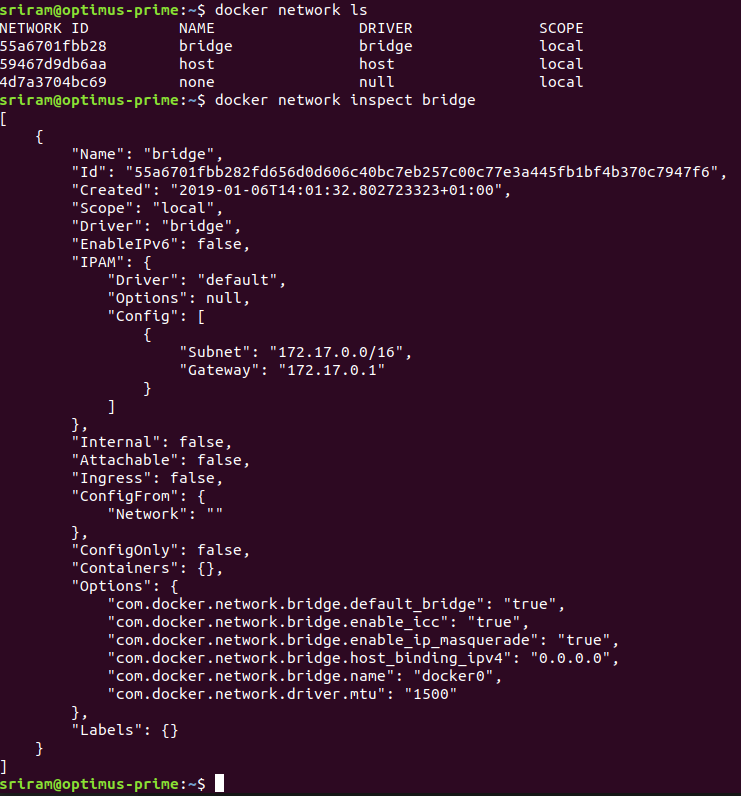
# By default, docker will add all running containers to default bridge network
# To inspect docker bridge network, use below command
docker network inspect bridge
Creating a custom docker network
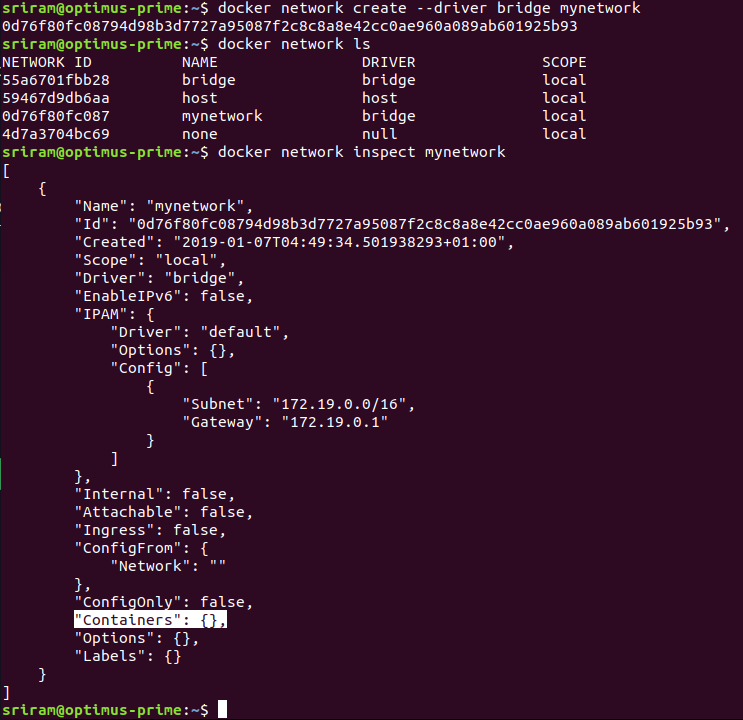
How to add container to a custom Network
# To run a docker container and join to a custom bridge network, use --net flag
docker container run --rm --itd --name <container_name> --net <network_name>
How to know the IP address of a running container
docker exec <container_name> ifconfig
docker exec <container_name> ip -a
References
To-DO
5 - Volumes
Nexus
Sonatype Nexus Docker with persisent data
chown -R 200 /home/sriram.yeluri/Data/NEXUS_DATA
docker run -d \
-p 8081:8081 \
--name nexus \
-v /home/sriram.yeluri/Data/NEXUS_DATA:/nexus-data \
sonatype/nexus3
Jenkins
Jenkins with persisent data
docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 \
--name jenkins \
-v /home/sriram.yeluri/Data/JENKINS_HOME:/var/jenkins_home \
jenkins
docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 \
--name jenkins \
-v /home/sriram.yeluri/Data/JENKINS_HOME:/var/jenkins_home \
jenkins/jenkins:lts
Jenkins Operations Center - JOC
docker run -p 8089:8080 -p 50001:50000 \
--name cjoc \
-v /home/sriram.yeluri/Data/JENKINS_OC_HOME:/var/jenkins_home \
cloudbees/jenkins-operations-center
#Initial secret can be found at below path
/var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Postgres
docker run \
--name postgres \
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=secret \
-d postgres \
-v /home/sriram.yeluri/Data/PG_DATA:/var/lib/postgresql/data